My notes on MongoDB
Intro
MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database. It is one of the most powerful NoSQL systems and databases around, today.
Key Features :
Here is the key features of MongoDB :
- MongoDB is free to use.
- MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, meaning fields can vary from document to document and data structure can be changed over time
- The document model maps to the objects in your application code, making data easy to work with
- Ad hoc queries, indexing, and real time aggregation provide powerful ways to access and analyze your data
- MongoDB is a distributed database at its core, so high availability, horizontal scaling, and geographic distribution are built in and easy to use
source: MongoDB Website
Terminology
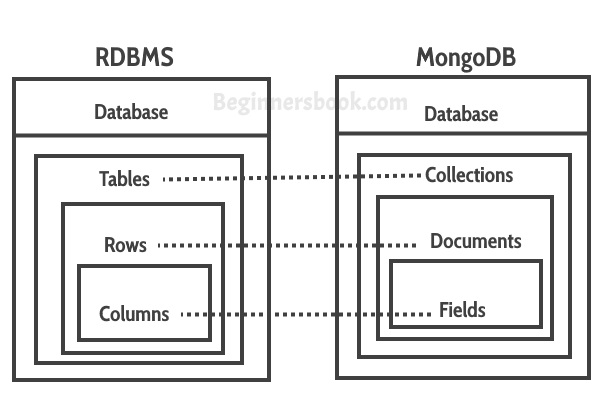
source: beginnersbook.com
database :
A database serves as a namespace for collections. It is similar to database in RDBMS. A single MongoDB server typically has multiple databases. Collections for same application should be in one database.
collection :
Collections store individual records called documents. It is the equivalent of an RDBMS table. Collections do not enforce a schema. Documents within a collection can have different fields. Typically, all documents in a collection have a similar or related purpose.
document :
Document is the basic unit of storage data. They are more oftenly referred to as Objects. They are analogous to JSON objects but exist in the database in BSON format.
source: MongoDB Docs
MongoDB supports a range of scalar value types such as : string, null, integer, double, and decimal, as well as document values, and array values.
note : All documents in MongoDB must contain this _id field. This is the unique identifier for a given document within a collection. If we don’t supply the value, MongoDB will automatically create one for us.
Example:
{
"_id": "5553a98ce4b02cf7150dee1f",
"st": "x+50600-002700",
"position": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [
-2.7,
50.6
]
},
"elevation": 9999,
"callLetters": "BUOY",
"qualityControlProcess": "V020",
"dataSource": "4",
"type": "FM-13",
"airTemperature": {
"value": 999.9,
"quality": "9"
},
"wind": {
"direction": {
"angle": 999,
"quality": "9"
},
"type": "9",
"speed": {
"rate": 999.9,
"quality": "9"
}
}
}
cursor :
This is a pointer to the result set of a query. Clients can iterate through a cursor to retrieve results.
I will try to add primary key, index, table joins,* *aggregation* and *transactions* here soon
Core Components
mongod:
mongod is the primary daemon process for the MongoDB system. It handles data requests, manages data access, and performs background management operations.When we start the mongod process, it basically starts the MongoDB and run it in the background. mongod has several default parameters, such as storing data in /data/db and running on port 27017.
$ mongod --port 27017 --dbpath /var/lib/mongodb
2019-12-15T15:37:47.653+0600 I CONTROL [initandlisten] MongoDB starting : pid=4523 port=27017 dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb 64-bit host=talha-pc
2019-12-15T15:37:47.653+0600 I CONTROL [initandlisten] db version v3.6.3
...
2019-12-15T15:37:48.281+0600 I NETWORK [initandlisten] waiting for connections on port 27017
mongo:
mongo is an interactive JavaScript shell interface for MongoDB. It provides a powerful interface for us to test queries and operations directly with the database. The commands we run in mongo shell are actually making real database commands behind it. When we run mongo with no parameters, by deafult it connects to the localhost on port 27017.
$ mongo
MongoDB shell version v3.6.3
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB server version: 3.6.3
Server has startup warnings:
2019-12-15T15:41:29.671+0600 I STORAGE [initandlisten]
....
Here is some basic commands with examples in mongo shell
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
blog 0.000GB
> use blog
switched to db blog
> show collections
articles
users
tags
comments
> db
blog
> db.users.find()
[{"_id":ObjectId("5d4910d0aac3dee44cfb98ec"),"name":"Talha Ibne Imam","username":"talha","email":"talha@demo.com",},{"_id":ObjectId("5de4ea9caaeb9cb649ca6dc2"),"name":"Ruhul Amin","username":"sujon","email":"sujon@demo.com",}]
Note : The find() method returns a cursor to the results. We can use several cursor methods (i.e: limit, skip) to call on the returned cursor and get our desired results. i.e.:
> db.users.find({"name":"Talha"}, {"name":1, "email":1}).limit(2)
Security
Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a client. When access control is enabled, MongoDB requires all clients to authenticate themselves in order to determine their access.
MongoDB supports different client authentication mechanisms :
- SCRAM (We should alway must configure atleast SCRAM)
- X.509
- LDAP (for MongoDB Enterprise only)
- KERBEROS (for MongoDB Enterprise only)
By default, MongoDB starts without any authentication. When we open the mongo shell, we will see a warning as below
** WARNING: Access control is not enabled for the database.
** Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted.
It is because the access control is not enabled by default. Once access control is enabled, users must authenticate themselves. Here is a very good blog post on how to enable authentication on MongoDB. For more details on it, you can visit the official doc
Authorization
MongoDB uses Role-Based Access Control(RBAC). A user is granted one or more roles that determine the user’s access to database resources and operations.
- Each user has one or more Roles
- Each Role has one or more Privileges
- A Privilege represents a specified resource and the actions permitted on the resource
- A resource is a database, collection, set of collections, or the cluster
- An action specifies the operation allowed on the resource
MongoDB provides built-in roles that provide set of privileges commonly needed in a database system. We can also create and modify user-defined roles if these built-in-roles cannot provide the desired set of privileges.
Tools
Binary Import/Export :
- mongodump : Which outputs BSON representations of MongoDB
- mongorestore : Which restores BSON representation in MongoDB into MongoDB collections
Data Import/Export :
- mongoexport : Which outputs JSON or CSV representations of MongoDB collections
- mongoimport : Which takes the JSON or the CSV representations and creates a MongoDB collection from it